Know the different levels/modes of RAID (0,1,2,3,4,5,6)
The full form of RAID is (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a disk storage technology that combines multiple physical drives into one unit having multiple levels. It creates redundancy which is a very important parameter in critical applications. It also improves the performance of the system.
As it has been wisely said that It is the part of a wise man to keep himself today for tomorrow, and NOT TO PUT ALL HIS EGGS IN ONE BASKET which means that one should not concentrate all efforts and resources in one area as one could lose everything.
In the same way, while dealing with data if we store it on a single disk then due to catastrophic reason, might be storage stops working and you will lose everything because overall its electronic device and no one can guarantee the working of it.
Thus, to avoid this disaster it is advised to store data on multiple storage devices rather than to store it on a single disk. This is the main idea behind RAID.
Common terms used in RAID
Striping:
Data is split between multiple disks. Here the load is trying to be distributed equally among all the disks while eliminating the overload of any single dis. As we can simultaneously retrieve data from multiple disks it will improve the speed and thus performance increases.
Mirroring
Data is mirrored between multiple disks means copies of data are stored among different storage devices. This will increase redundancy and performance too.
Parity
Also referred to as a checksum. Parity is a calculated value used to mathematically rebuild data. This is a basic error detection technique. Here the extra bits are generated which are added along with the data and transmitted, they are specially used to detect any error during transmission of the data. It will affect fault tolerance of data.
RAID controllers:
They are used to control hard disk drives they are also called disk array controllers. They can be in the form of hardware as well as software but almost they are implemented in hardware RAID.
Differences between RAID levels/modes
According to the different combinations of the above-explained terms, the RAID can be classified into various categories. We will be discussing here only the most important ones. There were only 6 RAID Levels defined officially but as time advances more level types has been added. Thus, here we will be going to discuss standard RAID levels only.
1. RAID 0
In this type of RAID, data striping is used. The available data is distributed evenly across multiple disks which will increase the data processing speed. As only striping is implemented without using mirroring and parity thus this level doesn’t have any redundancy or fault-tolerance.
Suppose there is a failure in one of the disk arrays, it will result in total data loss as data is distributed among the disks and no duplicate data is available.
As no redundancy available these type of RAID levels is generally implemented in the application which requires fast performance but will do not require strict fault tolerance policy such as Computer Gaming, Scientific Computations etc.
2. RAID 1
In RAID 1 level only data mirroring is implemented without the use of striping and parity. Generally, the data is duplicated over another single disk or multiple disks. This level will provide redundancy but not performance or fault tolerance.
As the same data is available over multiple arrays thus read operation can be done from both disks thus making read operation faster but in the case of the write operation, the data must be written on all disks thus making the process slower.
These types are preferred in applications that require high availability such as mission-critical operations where disaster recovery is the most important parameter. If a critical error occurs in the first disk then all the traffic will be automatically switched to another disk preventing from discontinuing of process.
3. RAID 2
Here the data is striped into bits (not in block ) and written on multiple drives. Along with striping, the parity bits are also used for forwarding Error Correction generally called FEC. The type of FEC is Hamming Code. The parity bits are also stored on separate arrays/disks. Thus, it will require synchronizing all the disks to maintain the proper relationship between data bits and corresponding parity bits otherwise the main purpose of fault tolerance will not be satisfied.
This RAID type is very rarely used for implementation because of its complex nature.
4. RAID 3
This is somewhat like the RAID 2 type. The only difference is that the data being striped is in the form of bytes rather than bits. Also, it uses a dedicated disk for parity. The parity bytes are determined for each row of data. RAID 3 is rarely used like RAID 2 but has some advantages that are worth to be discussed here. The read speed is quite good and it has resistance to damage to one disk.
This type is preferred where a very small number of users want to access huge data, otherwise, it is not preferred at all.
5. RAID 4
This type is also like RAID 3 but the difference is that data is striped into blocks instead of bytes with a dedicated parity disk. As it has parity bits therefore in case of any loss, we could recover the data by using appropriate parity methods. It is also rarely used for practical implementation.
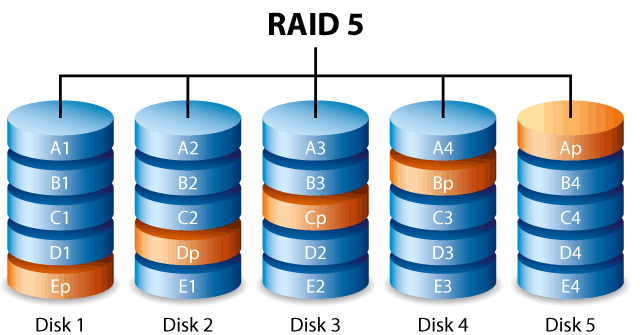
6. RAID 5
RAID 5 is most popular than all the RAID types we have discussed earlier. It has a slight difference from RAID 4. The data is striped into bocks and distributed over multiple disks. The most important point to be noted here is that the parity bits are also distributed among the same disks that are used to store data. Thus, no separate disk is used to store parity bits.
It requires a minimum of 3 disks to implement the RAID 5 type. Here also read process is very fast but write process is somewhat slow. This type of RAID is most commonly preferred for file and application servers. This RAID type can withstand a single drive failure condition
5. RAID 6
This type is very similar to RAID 5 but the slight difference is in storing parity bits, otherwise, all the architecture is the same. The one parity bit is written two times on two separate drives instead of a single drive. Thus, it can provide an additional level of redundancy than RAID 5.
Due to this strategic difference, it will require 4 minimum disk drives and can withstand two drives failure. In the real world, the two-disk failure simultaneously is having a very low probability. It is more secure than RAID 5.
RAID 6 is having overall good performance, good security than the remaining all RAID types we discussed, thus it is preferred to RAID 5 in file and application servers.
Conclusion
RAID is just technology used for improving data processing. It makes use of methods such as data striping, mirroring and use of parity checking bits over multiple disks instead of a single disk.
As seen as we go from RAID 0 to RAID 6, we will get some advantage in the form of either Performance, Redundancy or Fault-Tolerance. RAID 6 is most widely used because of its advantages.
Also, one should keep in mind that RAID should not replace Data-Backup. Even many RAID types protect from single disk failure then also for mission-critical operation one should require whole data thus Data-Backup is mandatory in such cases.
